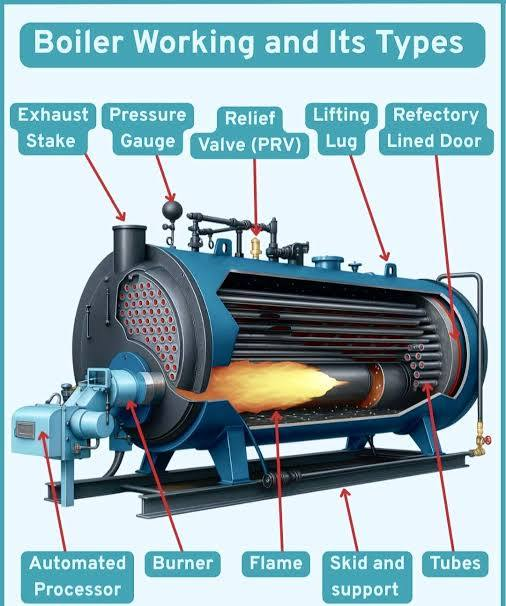
A Combustion Processes and Heat Transmission course for marine engineering describes the fundamental principles of thermodynamics, fuel combustion, and heat transfer as applied to ship propulsion and power systems, focusing on how to analyze, design, and optimize systems like boilers and engines for efficiency and emission reduction, including practical aspects like using new fuels and managing waste heat recovery
- Trainer: Albertina Antindi
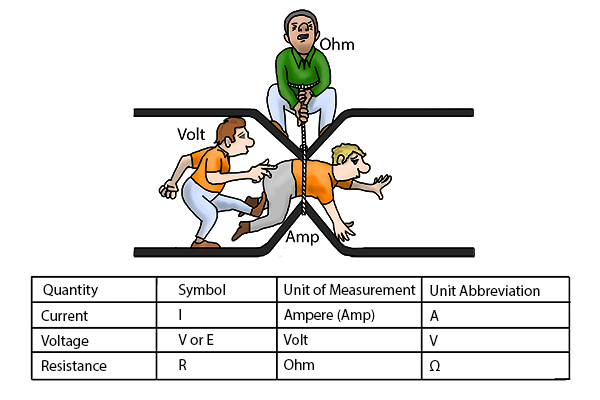
Marine electrical basics cover systems that generate, distribute, and use electricity on a vessel, relying on both Direct Current (DC) from batteries for starting and basic systems and Alternating Current (AC) for larger appliances and shore power, which requires generators and inverters. Key components include power sources (batteries, generators), circuit breakers for safety, wiring and cables, and panel boards for distribution. Proper sizing, installation, maintenance, and use of waterproof, corrosion-resistant materials are crucial for safety, reliability, and comfort in the challenging marine environment.
- Trainer: Benjamin Paulus
Study of Marine Auxiliary Systems
Objectives
|
ü States the approximate Carbon content and uses of Mild steel, Medium-carbon steel, High-carbon Steel and Cast iron |
|
ü Explains the principal difference between grey and white cast iron |
|
ü Sketches graphs showing the effect of varying carbon content on the tensile strength, Ductility, Malleability and Hardness of steels. |
- Trainer: Eliakim Hangala
Basic machine operation safety and maintenance.
- Trainer: Eliakim Hangala